Introduction:
The Clarifier, or Settling Tank, is a crucial component in the sewage treatment process, designed to separate solid sludge from treated water through sedimentation. It ensures that bacterial flocs settle efficiently while preventing turbulence, allowing for the collection of sludge and the discharge of clarified water. Proper operation of the clarifier is essential to maintaining a balanced biological process in the treatment plant, preventing microorganism loss, and ensuring smooth wastewater processing.
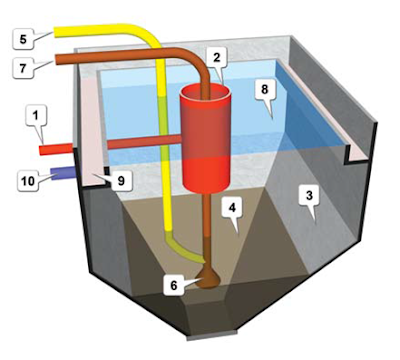
CLARIFIER/ SETTLING TANK
1 The sewage inlet pipe brings sewage from the aeration tank.
2 The center-feed well takes this incoming sewage and gently releases it in the settling tank, without causing any disturbance or turbulence.
3 The sludge is only slightly heavier than water; so it takes time to sink. It slides down the steeply sloped walls of the tank toward the center of the bottom.
4 The bacterial flocs7 collect here in high concentration.
5 The sludge delivery pipe delivers the slurry to the pumps (6).
6 There are two identical pumps. Since the flow rate of these pumps is fixed, they need to be turned off periodically to bring down the net flow rate to achieve the desired MLSS ratio. This is a critical operation, because if flocs remain in the settling tank for more than 30 minutes, the microorganisms die due to lack of oxygen.
7 The T-shaped header assemble joins the outlet pipes of both pumps, and delivers the sludge to the aeration tank.
8 The clear water rises to the top of the tank.
9 Typically the tank has launders on all four sides.
10 The clarified water pipe takes the decanted water to the clarified water sump.
CLARIFIED WATER SUMP
Overflow water from the clarifier is collected in an intermediate clarified water sump, This sump acts as a buffer tank between the secondary and the tertiary treatment stages in an STP.
In a well-run STP, the treated water quality at this stage is good enough for reuse on lawns and gardens with sufficient disinfection, and water for garden use may be directly taken from this sump, without having to overload the tertiary units.
Also, during lean inflow periods to the STP, backwashing of the filters is carried out. At this time, this tank must hold sufficient buffer stock of water for backwash purposes.
Final Words:
Efficient clarifier operation, including timely sludge removal and maintaining optimal flow rates, is key to ensuring the quality of treated water. The clarified water sump acts as a buffer, facilitating the reuse of treated water for landscaping and aiding in system maintenance. A well-managed clarifier and sump improve the overall efficiency of a sewage treatment plant, reducing environmental impact and optimizing water resource utilization.

Comments
Post a Comment